
Each hydrogen atom needs one more electron, which we can represent with a pair of dots next to each hydrogen atom.
#Simple diagrams of atoms full#
We now need to add pairs of electrons to the hydrogen atoms to give them a full outer shell of electrons. How do you draw Lewis dot diagrams?Īs there are three hydrogen atoms, we've used up six electrons to form the bonds. In the next section, we'll look at some more complicated examples of drawing Lewis dot diagrams. However, it can get a little more tricky for more complex molecules and so there is a set procedure that is helpful to follow. You can see this in the Lewis dot diagram below.ĭrawing Lewis dot diagrams for simple molecules like oxygen or methane is fairly straightforward. Each oxygen atom also has two lone pairs of electrons. An oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen atoms, joined by a double covalent bond. We'll start with the Lewis dot diagram for an oxygen molecule, O2. Let's look at some simple Lewis dot diagrams to help you get an understanding of how they work.
Overall, Lewis dot diagrams are a crucial tool for understanding the valence electrons and bonding patterns in molecules, making them an essential part of any chemistry student's toolkit. The Lewis dot diagram for CO2 shows that each oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons, while the carbon atom has no lone pairs but instead has two double bonds with the oxygen atoms. The Lewis dot diagram for water shows two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom, indicating that it has a total of eight valence electrons.Īnother example is carbon dioxide (CO2), which has one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. For instance, a simple molecule like water (H2O) has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Now, let's take a closer look at some examples of Lewis dot diagrams. Lewis dot diagrams are based on the octet rule, which states that atoms are most stable when they have a full outer shell of eight valence electrons.Bonded pairs of electrons are represented as lines, with a single line representing a single covalent bond and two lines representing a double covalent bond.Electrons are represented as dots, with two dots side by side representing a lone pair of electrons.Here are some key features of Lewis dot diagrams:
They show the atoms in a molecule, along with the number, position, and arrangement of the valence electrons. Lewis dot diagrams are also known as Lewis structures, Lewis dot structures, or electron dot structures. In the previous section, we introduced the concept of a Lewis dot diagram as a simplified way of representing a molecule's valence electrons. Understanding Lewis Dot Diagrams: Examples and Key Features
#Simple diagrams of atoms how to#
So if you're a chemistry student or just someone curious about the world around you, read on to learn how to draw and interpret Lewis dot diagrams for different molecules! What are Lewis dot diagrams? Plus, drawing Lewis dot diagrams is a great way to simplify complex chemical structures and make them easier to understand. This information is crucial in predicting a molecule's reactivity and properties. Finally, we'll consider the importance of these diagrams in understanding chemical structures.īy using Lewis dot diagrams, we can easily determine the number of valence electrons in a molecule and how they are arranged. Then, we'll learn how to draw Lewis dot diagrams. We'll start by explaining what they are before delving into some common examples. In this article, we'll explore Lewis dot diagrams in chemistry. It shows the arrangement of atoms, valence electrons, and their bonding. Enter the Lewis dot diagram.Ī Lewis dot diagram is a simplified representation of a molecule's valence electrons. However, drawing out all of the electron shells can be complex and time-consuming, especially for larger molecules.

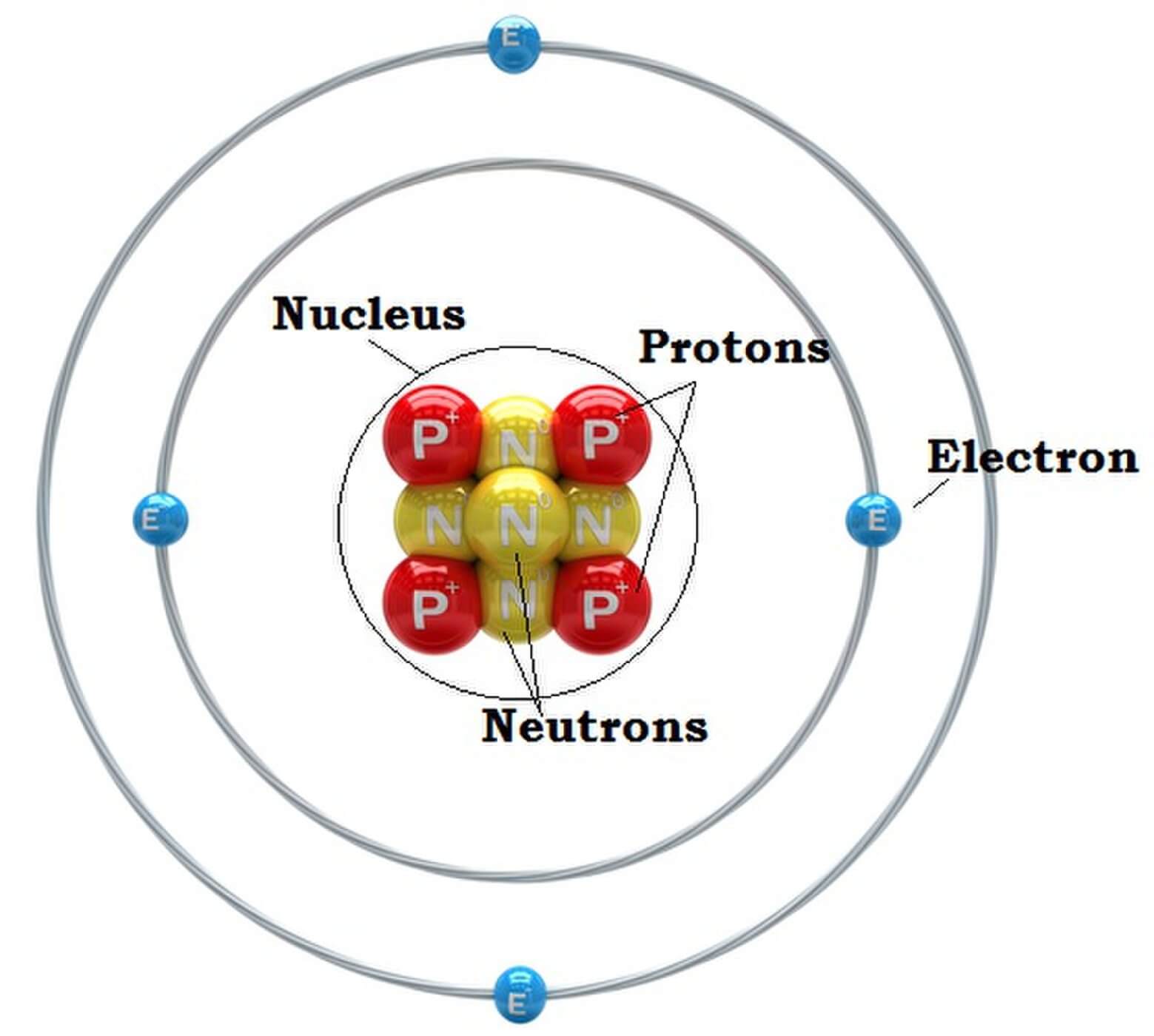
Valence electrons determine a species' properties and how it reacts with other substances. When studying chemical species, understanding the arrangement of their valence electrons is key.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
